A hybrid FPGA consists of a combination of coarse-grained and fine-grained reconfigurable elements.
The fine-grained resources in the FPGA consistof a grid of identical configurable logic blocks (CLBs), each containing look up tables (LUTs) and flip flops (FFs).
Coarse-grained elements can implement a specific function more efficiently than fine-grained programmable logic. DSP, memory and floating point unit (FPU) are examples of the coarse-grained embedded blocks (EBs). Figure 1. shows an example of hybrid FPGA.
¡@
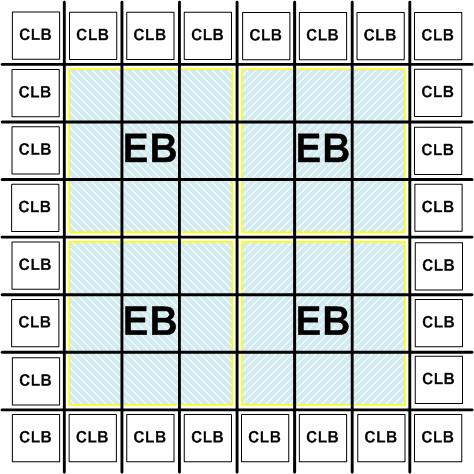 Figure 1. An example of hybrid FPGA |